Data for Growth: Proven Ways SMEs Can Use AI & Analytics to Outperform Competitors
Once upon a time, in the bustling city of Techville, there lived a visionary business owner named Sarah. Sarah had recently stepped into the role of manager at a charming, family-owned restaurant named "The Hungry Byte."
The restaurant had a loyal customer base, but it operated in a very traditional manner: customers would walk up to the counter, place their orders, and wait patiently for their meals. There was no online ordering, no loyalty program, and certainly no data-driven decision-making. Sarah, with her background in technology and a passion for innovation, saw immense potential to transform The Hungry Byte into a modern, competitive eatery.
She dreamed of using data analytics and Artificial Intelligence to elevate the customer experience, streamline operations, and boost profitability. However, as she began this journey, it became clear that the road was filled with obstacles—obstacles that numerous small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) encounter when seeking to harness the potential of data and AI.
There was no system to track which dishes were popular, no way to predict busy hours, and no insight into customer preferences…
Sarah stared at the old cash register, its keys worn from years of use. This is where it all starts, she thought. The Hungry Byte was stuck in the past. Customers waited—sometimes too long—while the kitchen hustled to keep up with orders. There was no system to track which dishes were popular, no way to predict busy hours, and no insight into customer preferences. Inventory was managed on paper, and marketing was limited to flyers and word-of-mouth.
Sarah felt overwhelmed as she grappled with insufficient data infrastructure and the daunting task of modernizing a traditional business. But she was determined. She envisioned a future where The Hungry Byte could anticipate customer needs, optimize its menu, and personalize promotions—all powered by data and AI.
This is the story of how Sarah—and SMEs like hers—can overcome these challenges and unlock the transformative power of data analytics and GenAI. In the following sections, we’ll explore the barriers SMEs face, the types of data they can leverage, practical applications of analytics and AI, and actionable steps to get started.
By the end, you will see that even the smallest businesses can harness these technologies to thrive in a competitive market.
Challenges Faced by SMEs
Sarah’s first hurdle was clear: SMEs like The Hungry Byte often lack the resources and expertise to dive into data analytics and AI. Here are the most common barriers:
Limited Expertise: Many SMEs don’t have in-house data scientists or AI specialists. Sarah, for instance, was tech-savvy but not an expert in analytics.
Tight Budgets: Integrating advanced software solutions like Salesforce (CRMs), SAP (ERPs), or HubSpot (marketing automation) can be costly. The Hungry Byte couldn’t afford a major tech overhaul.
Poor Data Quality: Without existing databases, customer records, or digital feedback systems, SMEs struggle to collect and organize data. Sarah had no historical sales data or customer profiles to work with.
These challenges often arise from a lack of awareness, fear of complexity, or simply not knowing where to start. Many SMEs believe that data analytics and AI are reserved for large corporations with deep pockets. However, this mindset is becoming outdated. The rise of GenAI tools and open-source solutions has democratized access to powerful technologies. For example:
Affordable AI APIs: Tools like OpenAI’s GPT-4 allow SMEs to integrate AI-powered features (e.g., chatbots or recommendation engines) without building models from scratch.
Open-Source Solutions: Platforms like Akaunting offer free or low-cost sales tracking and accounting software, making it easier to digitize financial data.
Cloud-Based Analytics: Services like Google Analytics or Microsoft Power BI provide scalable, pay-as-you-go options for data analysis.
Sarah realized that she didn’t need to break the bank to get started. By leveraging these tools, she could begin collecting and analyzing data incrementally, setting the foundation for more advanced AI applications down the road.
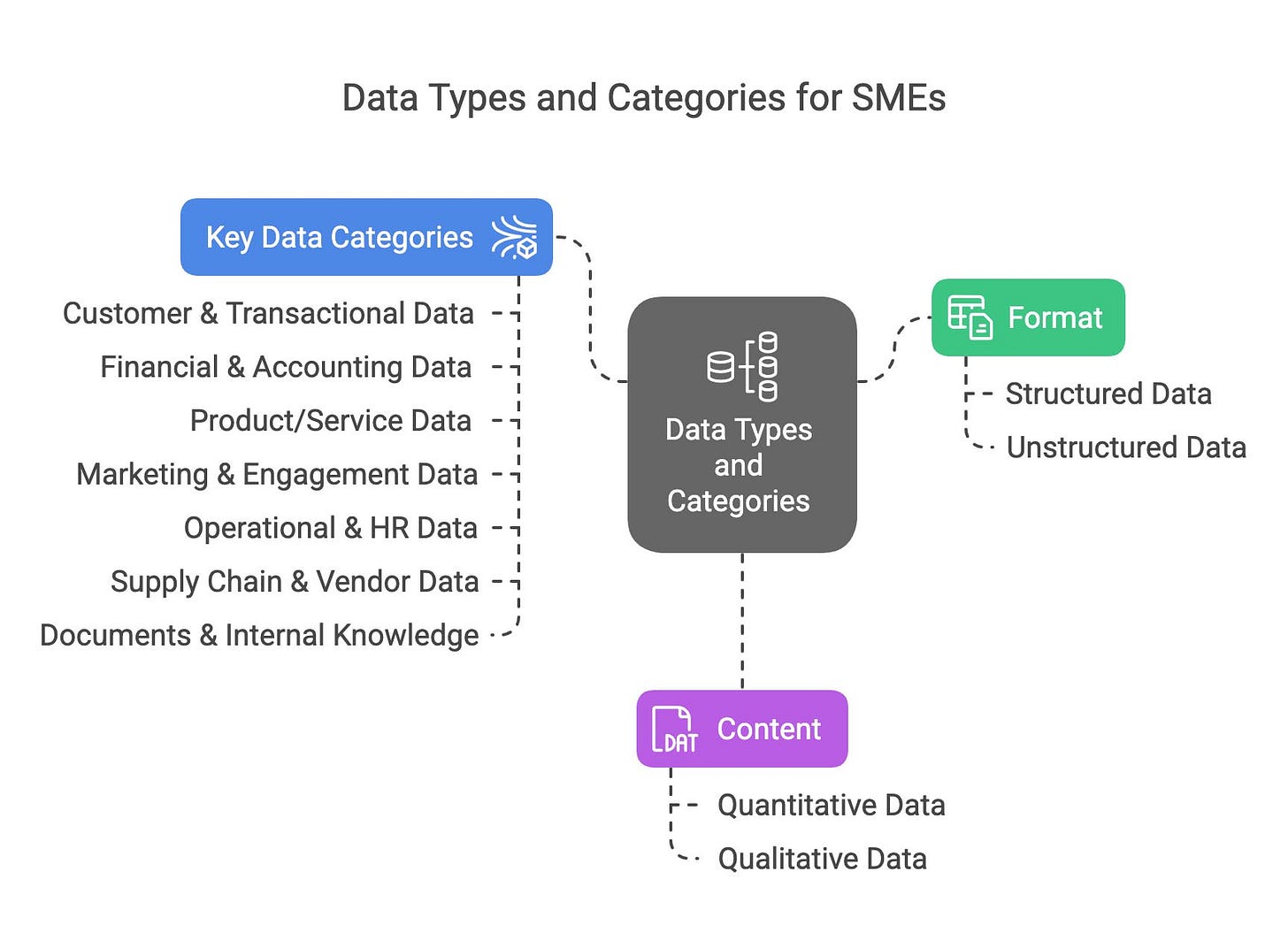
Types of Data SMEs Generate
Before Sarah could transform The Hungry Byte, she needed to understand the types of data her business was generating—and what she should be collecting. For SMEs, data can be grouped into two primary dimensions: format (how it’s structured) and content (what it measures).
Format: Structured vs. Unstructured Data
Structured Data: Highly organized, stored in fixed fields (like tables or spreadsheets), and easy to search or analyze with tools like Excel or databases.
Example at The Hungry Byte: Sales transactions in a point-of-sale (POS) system, showing each order’s date, time, items, and total amount.
Why it’s useful: Ideal for analytics, such as calculating average order values or identifying peak hours.
Unstructured Data: Less organized, often in free-form text, images, or videos, requiring advanced processing to extract insights.
Example at The Hungry Byte: Customer reviews on social media or handwritten feedback cards describing the dining experience.
Why it’s useful: Perfect for GenAI applications, like generating responses to reviews or analyzing sentiment.
Content: Quantitative vs. Qualitative Data
Quantitative Data: Numerical, measurable data that supports statistical analysis.
Example at The Hungry Byte: Number of meals sold daily or the percentage of customers ordering dessert.
Why it’s useful: Drives analytics for trends, forecasts, and performance metrics.
Qualitative Data: Descriptive, non-numerical data that captures experiences, opinions, or preferences.
Example at The Hungry Byte: Comments praising the restaurant’s cozy ambiance or suggesting faster service.
Why it’s useful: Fuels GenAI for creating personalized marketing or improving customer experiences.
Key Data Categories for SMEs
Using The Hungry Byte as an example, Sarah identified the following data categories to collect, aligning with both analytics and AI goals:
Customer & Transactional Data
Customer profiles (names, emails, visit frequency), purchase history (items ordered, amounts spent), feedback (reviews, ratings).
Example: A loyalty card capturing customer emails and their favorite dishes.
Use case: Analytics for segmenting customers; AI for personalized promotions.
Financial & Accounting Data
Invoices, revenue reports, expense logs, cash flow statements.
Example: Daily revenue totals from the POS system.
Use case: Analytics for budgeting; AI for automated financial summaries.
Product/Service Data
Menu item details (prices, ingredients), inventory levels, sales per item.
Example: Stock levels of fresh ingredients like tomatoes.
Use case: Analytics for inventory forecasting; AI for dynamic menu suggestions.
Marketing & Engagement Data
Social media metrics (likes, shares), email campaign performance (open rates), website traffic.
Example: Clicks on a promotional email offering a dessert deal.
Use case: Analytics for campaign optimization; AI for crafting ad copy.
Operational & HR Data
Staff schedules, performance reviews, payroll records.
Example: Shift logs showing who worked during busy hours.
Use case: Analytics for staffing efficiency; AI for training guides.
Supply Chain & Vendor Data
Supplier contracts, delivery schedules, procurement logs.
Example: Delivery records for fresh produce.
Use case: Analytics for supply chain optimization; AI for vendor communications.
Documents & Internal Knowledge
Recipes, training manuals, standard operating procedures (SOPs).
Example: A recipe book for signature dishes.
Use case: Analytics for process improvements; AI for generating SOPs or chatbots.
By prioritizing these categories, Sarah could start small—focusing on customer and transactional data—and build a robust data foundation for analytics and AI.
Practical Applications of Data Analytics and AI
Once Sarah began collecting data at The Hungry Byte, she needed to translate it into actionable outcomes. Data analytics and AI offer SMEs powerful ways to achieve key business goals: improving efficiency, growing revenue, enhancing quality, reducing risks, and cutting costs.
Below, we explore how SMEs can apply these technologies, using The Hungry Byte as a lens to make the use cases tangible and inspiring. Each goal includes analytics and GenAI applications, with real-world examples to show what’s possible.
1. Improving Efficiency
Efficiency is about doing more with less, and Sarah quickly saw how data analytics and AI could streamline The Hungry Byte’s operations. Analytics can reveal patterns that optimize resource use, such as analyzing sales data to schedule staff only when needed.
For instance, a café studying its sales records could discover that morning hours are the busiest, allowing it to reduce afternoon staffing and cut labor costs by 15%. Sarah could do the same by tracking when customers visit most, ensuring her team is ready for rushes without overstaffing.
GenAI takes this further by automating repetitive tasks. Tools like Agent Assist or virtual assistants can handle customer inquiries. Sarah could start by setting up a simple chatbot on her website to answer common questions like “What’s on the menu?” or “Do you take reservations?” These tools are accessible and can save hours each week, making efficiency gains immediate and measurable.
2. Growing Revenue
For SMEs like The Hungry Byte, revenue growth often hinges on understanding and delighting customers. Data analytics excels at segmenting customers based on their purchase history, enabling targeted promotions that drive sales. A group of marketers used customer data to craft personalized email campaigns, boosting sales by 20% by offering deals on items customers already loved.
Sarah could analyze which dishes sell best to certain demographics, then send tailored offers—like a discount on vegan dishes to plant-based diners. GenAI amplifies this with tools like personalized recommendations and price optimization. By analyzing customer preferences, AI can suggest add-ons, such as recommending a dessert with a main course, increasing order values.
Sarah could also use GenAI for media intelligence, scanning social media to identify trending flavors, or automate business processes like email marketing to re-engage lapsed customers. Starting with a free tool like Google Analytics to track customer behavior or a low-cost AI platform for email automation, SMEs can see revenue lift without a big investment.
3. Enhancing Quality
Quality is a differentiator for SMEs, and both analytics and GenAI can elevate the customer experience. Analytics helps by monitoring feedback to pinpoint areas for improvement. A hotel chain using sentiment analysis on guest reviews can identify service gaps, improving satisfaction by at least 10% after training staff on key issues.
Sarah could analyze online reviews to see if slow service is a recurring complaint, then adjust kitchen workflows. GenAI, meanwhile, shines in creating high-quality content. Tools like sales and marketing content creation or report generation can produce compelling menu descriptions or social media posts. A design SME used ChatGPT to draft 80% of its marketing content, with human editors polishing the final output, saving time while maintaining brand voice.
SMEs can start by collecting feedback via free survey tools like Google Forms and experimenting with AI content tools to enhance their offerings, making quality a competitive edge.
4. Reducing Risks
Risk management is critical for SMEs, where a single misstep can be costly. Data analytics can identify anomalies in financial data to help prevent fraud. For example, an accounting firm can flag irregular transactions, reducing fraud by at least 25%. Sarah could use analytics to spot unusual patterns, like discrepancies in daily sales, ensuring her finances stay secure. AI enhances this with tools like fraud detection and pattern recognition, automating compliance checks or monitoring for security threats.
SMEs can begin with basic analytics in Excel to track financial anomalies and explore affordable AI APIs for automated checks. These steps mitigate risks without requiring a large team or budget, giving SMEs peace of mind.
5. Cutting Costs
Cost reduction is a priority for resource-constrained SMEs, and analytics and GenAI offer smart ways to save. Analytics can optimize supply chain logistics, reducing waste and overstock. Sarah could analyze ingredient usage to avoid spoilage, cutting food costs.
GenAI further reduces expenses through automation, such as AI-enabled call centers or real-time process diagnosis. Sarah could use GenAI for automated content tagging, organizing customer feedback for quick analysis, or automate data entry for sales records.
SMEs can start with free tools like Google Sheets for inventory tracking and try AI automation platforms with low-cost plans. These approaches deliver cost savings that directly impact the bottom line, making them highly appealing for SMEs.
Conclusion
Sarah’s journey with The Hungry Byte mirrors the path many SMEs must take to embrace data analytics and AI. By starting small—collecting basic data, using affordable tools, and fostering a data-driven culture—businesses can overcome challenges and unlock powerful benefits: improved efficiency, increased revenue, enhanced quality, reduced risks, and lower costs.
The key is to start now. Identify one area where data can make an immediate impact—whether it’s tracking sales, understanding customers, or automating a task—and build from there. With each step, your business will grow smarter, more agile, and ready for the future.